Class to compute Spectrophores™.
- Since
- Version 2.3
Introduction
Spectrophores™ are one-dimensional descriptors generated from the property fields surrounding the molecules. The technology allows the accurate description of molecules in terms of their surface properties or fields. Comparison of molecules’ property fields provides a robust structure-independent method of aligning actives from different chemical classes. When applied to molecules such as ligands and drugs, Spectrophores™ can be used as powerful molecular descriptors in the fields of chemoinformatics, virtual screening, and QSAR modeling.
The computation of Spectrophores™ is independent of the position and orientation of the molecule and this enables easy and fast comparison of Spectrophores™ between different molecules. Molecules having similar three-dimensional properties and shapes always yield similar Spectrophores™.
A Spectrophore™ is calculated by surrounding the three-dimensional conformation of the molecule by a three-dimensional arrangement of points, followed by calculating the interaction between each of the atom properties and the surrounding the points. The three-dimensional arrangement of the points surrounding the molecule can be regarded as an ‘artificial’ cage or receptor, and the interaction calculated between the molecule and the cage can be regarded as an artificial representation of an affinity value between molecule and cage. Because the calculated interaction is dependent on the relative orientation of the molecule within the cage, the molecule is rotated in discrete angles and the most favorable interaction value is kept as final result. The angular stepsize at which the molecule is rotated along its three axis can be specified by the user and influences the accuracy of the method.
Atomic properties
The calculation of a Spectrophore™ starts by calculating the atomic contributions of each property from which one wants to calculate a Spectrophore™ from. In the current implementation, four atomic properties are converted into a Spectrophore™; these four properties include the atomic partial charges, the atomic lipohilicities, the atomic shape deviations and the atomic electrophilicities.
The atomic partial charges and atomic electrophilicity properties are calculated using the electronegativity equalisation method (EEM) as described by Bultinck and coworkers (J. Phys. Chem. 2002, A106, 7895-7901; J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 422-428). The following table lists the atomic electronegativity and hardness parameters that are used in the current implementation of the EEM method:
| Atom symbol | Atomic electronegativity | Atomic hardness |
| H | 0.20606 | 0.65971 |
| C | 0.36237 | 0.32966 |
| N | 0.49279 | 0.34519 |
| O | 0.73013 | 0.54428 |
| F | 0.72052 | 0.72664 |
| S | 0.62020 | 0.20640 |
| Cl | 0.36237 | 0.32966 |
| Br | 0.70052 | 0.54554 |
| I | 0.68052 | 0.30664 |
| Default | 0.36237 | 0.32966 |
Atomic lipophilic potential parameters are calculated using a rule-based method using parameters from the following table. These parameters were obtained by fitting against the logP values of 10,881 molecules.
| Atom | Lipophilicity parameter |
| H bound to C | -0.018 |
| H bound to heteroatom | -0.374 |
| C | +0.271 |
| N | -0.137 |
| O | -0.321 |
| F | +0.217 |
| S | +0.385 |
| Cl | +0.632 |
| Br | +0.815 |
| I | +0.198 |
| Default | -0.175 |
Finally, the atomic shape deviation is generated by calculating, for each atom, the atom’s deviation from the average molecular radius. This is done in a four steps process:
- The molecular center of geometry (COG) is calculated;
- The distances between each atom and the molecular COG are calculated;
- The average molecular radius is calculated by averaging all the atomic distances.
- The distances between each atom and the COG are then divided by the average molecular radius and centered on zero.
Interaction between the atoms and cage points
Following the calculation of all required atomic properties, the next step in the calculation of a Spectrophore™ consists of determining the total interaction value V(c,p) between each of the atomic contributions of property p with a set of interaction points on an artificial cage c surrounding the molecular conformation. For this purpose, each of these interaction points i on cage c is assigned a value P(c,i) which is either +1 or -1, with the constraint that the sum of all interaction points on a particular cage should be zero. In a typical Spectrophore™ calculation, a cage is represented as a rectangular box encompassing the molecular conformation in all three dimensions, with the centers of the box edges being the interaction points. Such a configuration gives twelve interaction points per cage, and, in the case of a non-stereospecific distribution of the interaction points, leads to 12 different cages. Although there are no particular requirements as to the dimensions of the rectangular cage, the distance between the interaction points and the geometrical extremes of the molecule should be such that a meaningful interaction value between each cage point and the molecular entity can be calculated. In this respect, the default dimensions of the cage are constantly adjusted to enclose the molecule at a minimum distance of 3 Å along all dimensions. This cage size can be modified by the user and influences the resolution of the Spectrophore™.
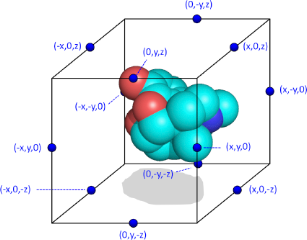
Schematic representation of a molecule surrounded by the artifical cage
The total interaction value V(c,p) between the atomic contribution values A(j,p) of property p for a given molecular conformation and the cage interaction values P(c,i) for a given cage c is calculated according a standard interaction energy equation. It takes into account the Euclidean distance between each atom and each cage point. This total interaction V(c,p) for a given property p and cage c for a given molecular conformation is minimized by sampling the molecular orientation along the three axis in angular steps and the calculation of the interaction value for each orientation within the cage. The final total interaction V(c,p) for a given cage c and property p corresponds to the lowest interaction value obtained this way, and corresponds to the c’th value in the one-dimensional Spectrophore™ vector calculated for molecular property p. As a result, a Spectrophore™ is organized as a vector of minimized interaction values V, each of these organized in order of cages and property values. Since for a typical Spectrophore™ implementation twelve different cages are used, the total length of a Spectrophore™ vector equals to 12 times the number of properties. Since four different properties are used in the current implementation (electrostatic, lipophilic, electrophilic potentials, and an additional shape index as described before), this leads to a total Spectrophore™ length of 48 real values per molecular conformation.
Since Spectrophore™ descriptors are dependent on the actual three-dimensional conformation of the molecule, a typical analysis includes the calculation of Spectrophores™ from a reasonable set of different conformations. It is then up to the user to decide on the most optimal strategy for processing the different Spectrophore™ vectors. In a typical virtual screening application, calculating the average Spectrophore™ vector from all conformations of a single molecule may be a good strategy; other applications have benefit from calculating a weighted average or the minimal values.
Accuracy
As already mentioned, the total interaction between cage and molecule for a given property is minimized by sampling the molecular orientation in angular steps of a certain magnitude. As a typical angular step size, 20º was found to be the best compromise between accuracy and computer speed. Larger steps sizes are faster to calculate but have the risk of missing the global interaction energy minimum, while smaller angular steps sizes do sample the rotational space more thoroughly but at a significant computational cost. The accuracy can be specified by the user using the OBSpectrophore::SetAccuracy(const OBSpectrophore::AccuracyOption) method.
Resolution
Spectrophores™ capture information about the property fields surrounding the molecule, and the amount of detail that needs to be captured can be regulated by the user. This is done by altering the minimal distance between the molecule and the surrounding cage. The resolution can be specified by the user with the OBSpectrophore::SetResolution(const double) method. The default distance along all dimensions is 3.0 Å. The larger the distance, the lower the resolution. With a higher resolution, more details of the property fields surrounding the molecule are contained by the Spectrophore™. On the contrary, low resolution settings may lead to a more general representation of the property fields, with little or no emphasis on small local variations within the fields. Using a low resolution can be the method of choice during the initial virtual screening experiments in order to get an initial, but not so discriminative, first selection. This initial selection can then further be refined during subsequent virtual screening steps using a higher resolution. In this setting, small local differences in the fields between pairs of molecules will be picked up much more easily.
The absolute values of the individual Spectrophore™ data points are dependent on the used resolution. Low resolution values lead to small values of the calculated individual Spectrophore™ data points, while high resolutions will lead to larger data values. It is therefore only meaningful to compare only Spectrophores™ that have been generated using the same resolution settings or after some kind of normalization is performed.
Computation time is not influenced by the specified resolution, hence the computation time is identical for all different resolution settings.
Stereospecificity
Some of the cages that are used to calculated Spectrophores™ have a stereospecific distribution of the interaction points. The resulting interaction valus resulting from these cages are therefore sensitive to the enantiomeric configuration of the molecule within the cage. The fact that both stereoselective as well as stereo non-selective cages can be used makes it possible to include or exclude stereospecificity in the virtual screening search. Depending on the desired output, the stereospecificity of Spectrophores™ can be specified by the user:
- No stereospecificity (default). Spectrophores™ are generated using cages that are not stereospecific. For most applications, these Spectrophores™ will suffice.
- Unique stereospecificity. Spectrophores™ are generated using unique stereospecific cages.
- Mirror stereospecificity. Mirror stereospecific Spectrophores™ are Spectrophores™ resulting from the mirror enantiomeric form of the input molecules.
The stereospecificity can be specified by the user using the OBSpectrophore::SetStereo(const OBSpectrophore::StereoOption) method.
The differences between the corresponding data points of unique and mirror stereospecific Spectrophores™ are very small and require very long calculation times to obtain a sufficiently high quality level. This increased quality level is triggered by the accuracy setting and will result in calculation times being increased by at least a factor 100. As a consequence, it is recommended to apply this increased accuracy only in combination with a limited number of molecules, and when the small differences between the stereospecific Spectrophores™ are really critical. However, for the vast majority of virtual screening applications, this increased accuracy is not required as long as it is not the intention to draw conclusions about differences in the underlying molecular stereoselectivity. Non-stereospecific Spectrophores™ will therefore suffice for most applications.
Normalisation
It may sometimes be desired to focus on the relative differences between the Spectrophore™ data points rather than focussing on the absolute differences. In these cases, normalization of Spectrophores™ may be required. The current implementation offers with the OBSpectrophore::SetNormalization(const OBSpectrophore::NormalizationOption) method the possibility to normalize in four different ways:
- No normalization (default);
- Normalization towards zero mean;
- Normalization towards standard deviation;
- Normalization towards zero mean and unit standard deviation.
In all these cases, normalization is performed on a ‘per-property’ basis, which means that the data points belonging to the same property set are treated as a single set and that normalization is only performed on the data points within each of these sets and not across all data points.
Normalization may be important when comparing the Spectrophores™ of charged molecules with those of neutral molecules. For molecules carrying a global positive charge, the resulting Spectrophore™ data points of the charge and electrophilicity properties will both be shifted in absolute value compared to the corresponding data points of the respective neutral species. Normalization of the Spectrophores™ removes the original magnitude differences for the data points corresponding to the charge and electrophilicity properties of charged and neutral species. Therefore, if the emphasis of the virtual screening consists of the identification of molecules with similar property fields without taking into account differences in absolute charge, then Spectrophores™ should be normalized towards zero mean. However, if absolute charge differences should be taken into account to differentiate between molecules, unnormalized Spectrophores™ are recommended.
- Since
- version 2.3

 1.8.13
1.8.13